Renal Transplant Donor
Contents
- Donor classification
- DBD,
- DCD
- Maastricht classification
- Prognosis
- Living donor
- Tissue typing and Crossmatch
- Graft function and survival
- Issues facing transplant
___________________________________
___________________________________
1. Classification of kidney donors
Living donor
- Related donors & unrelated donor
- Altruistic directed or Undirected donation
- Paired donation - single or multiple
Deceased donor
- Donation after Brain Death (DBD)
- Donation after cardiac death (DCD)
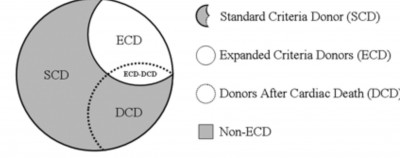
- Standard criteria donor (SCD)
- Expanded-criteria donor (ECD): a) donor ≥60 yr, or b) aged 50 to 59 yr and any two of three: Hypertension, SCr >1.5 mg/dl, or death by CVA
Link to the article from Clinical Journal of American Society of Nephrology:
___________________________________
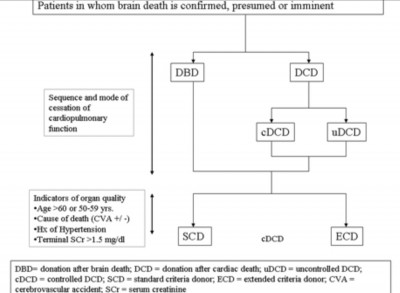
2. DBD: Donor with certified brain death,
but cardiac circulation and respiration maintained naturally or by ventilation, drugs, intra-aortic balloon pump, or extracorporeal machine oxygenation device.
___________________________________
3. Donation after cardiac death (DCD):
DCD (old term non–heart-beating donor.
___________________________________
4. Maastricht classification
- Cardiac arrest occurs before the organ harvest, spontaneously or controlled way. The DCD categories are of five types:
- Controlled DCD (cDCD), life support withdrawn in controlled operating room.
- Uncontrolled DCD (uDCD), cardiac arrest occurs requiring CPR during procurement of the organs.
- Brought in dead, unsuccessful resuscitation.
- Awaiting cardiac arrest - controlled.
- Cardiac arrest after brainstem death- Uncontrolled.
___________________________________
5. Prognosis of ECD, DBD & DCD
ECD kidney transplantation is associated with a significantly increased risk for delayed graft function (dialysis in the first week after transplant).
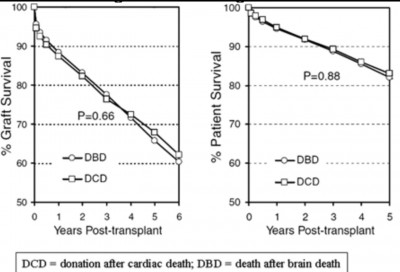
DCD kidney: both the graft and recipient survival are similar between DCD and DBD, but increase risk for delayed graft function was 42 to 51% in DCD compared with 24% in DBD kidney transplant recipients.
___________________________________
6. Living donor
Multiple Paired Exchanged Donor
Living donor
- Related donors
- Altruistic Unrelated directed Donor
- Undirected unrelated donor
(Paired donation - single or multiple)
Living Related Donor
The donor and the recipient have a biologic relationship. 1st & 2nd degree.
Unrelated Donor
- Spouse to spouse Emotional relationship.
- Directed, anonymous donor-specific recipient.
- Altruistic directed
- Undirected, anonymous donor to the waiting list.
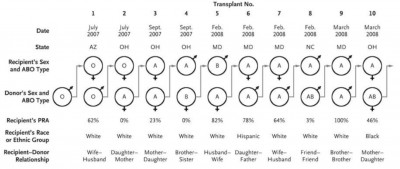
- Paired Exchange Donor: A pair of donor–recipient candidates (from the related or unrelated categories) exchange within each other for ABO compatibility or cross-match reactivity.
- Multiple Paired Exchanged Donor. This is paired exchange donation but involves more than two donor–recipient candidate pairs, as shown in the above figure.
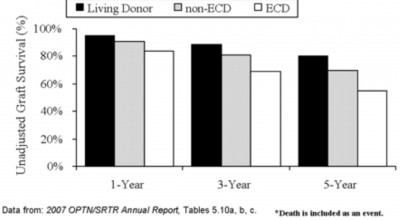
Graft survival rates for different types of kidney transplantation.
Unadjusted 1, 3, and 5yr kidney graft survival, by donor type: 2000–2005.
___________________________________
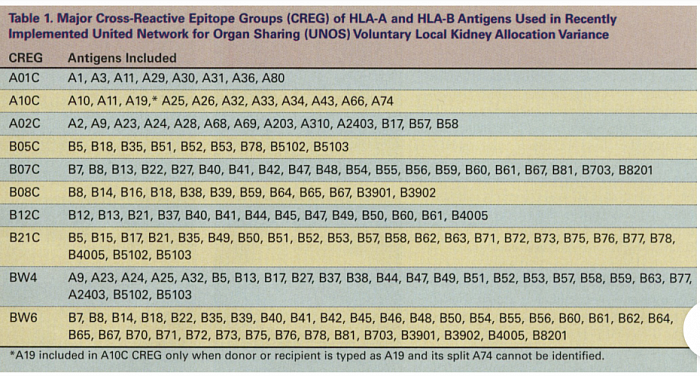
7. HLA typing and matching
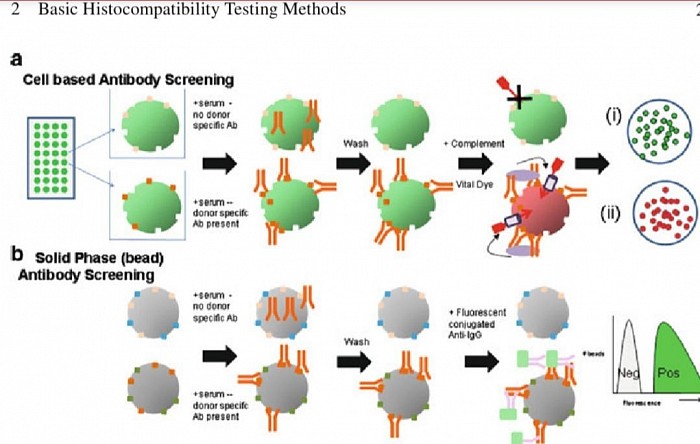
llustration of HLA typing: Schematic diagram of cell based and solid phase (bead based) antibody screening. ( a) Two representative wells are illustrated from the panel of cells that is used. Serum is added to each well in the panel. On the top the antibody in the serum does not bind to the cells on the bottom do nor specific antibody (DSA) does bind. Bound DSA remain after wash steps, so that when complement is added, it forms the membrane attack complex, killing the cell and allowing the vital dye is taken up by and visualized. No donor specific antibody leaves live cells (i), and when DSA are present, the vital dye identifies the dead cells (ii). ( b ) Serum is added to be adscoated with purified or recombinant HLA antigen. In this case, the antibody in the serum is only specific to the bead on the bottom. Only beads with DSA already bound will bind the secondary fluorescent anti-IgG marker. Increased fluorescence defines positive beads with DSA bound to them.
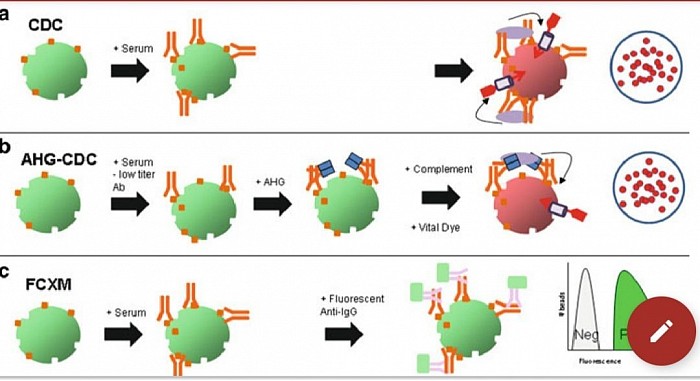
Evolution of basic crossmatching techniques (figure above). ( a) In an unenhanced complement dependent cytotoxicity crossmatch (CD), when high titer DSA is bound to the cell in suffi cient density, complement is activated, the cell is killed and the vital dye is taken up identifying the dead cells. ( b) With the AHG enhancement, lower titer antibody is less dense on the cell surface and would not naturally activate complement. Adding AHG increases the overall density of complement activating antibodies on a cell that already has some DSA bound, thereby allowing complement activation with subsequent cell death as with CDC alone. ( c) In FCXM, donor-specific antibody binds the cell and a second fluorescent antibody to human IgG is used to detect even small amounts of bound antibody. When run through a flow cytometer, the DSA (which may be complement or noncomplement binding) is measured as fluorescence on the cells.
The transplanted organ is a continuous source of HLA alloantigens that can induce a rejection response at any time after transplantation. Both direct and indirect alloactivation pathways are important in the generation of donor-specific cell- mediated cytotoxicity and delayed-type hypersensi- tivity-like mechanisms of allograft rejection. Conversely, the continuous presence of small num- bers of donor APC (referred to as microchimerism) may promote and maintain allograft tolerance, rather than transplant rejection.